The above profile for Lambeosaurus lambei covers its temporal range, fossil location, jaw morphology, and endocranial research, with additional palaeontological information and references provided below.
Lambeosaurus lambei was a large hadrosaurid, a Lambeosaurine duck-billed dinosaur part of the same group of hadrosaurs Parasaurolophus belongs to. Lambeosaurus was a herbivore, capable of moving both bipedally and quadrupedally on its powerful limbs. Lambeosaurus was named by palaeontologist William Parks in 1923 who also named Parasaurolophus walkeri and a host of other dinosaurs from Canada.

Fossilised remains of Lambeosaurus lambei have been found in Dinosaur Provincial Park, one of the best fossil localities in the world for fossilised dinosaur remains. Three species of Lambeosaurus are known: Lambeosaurus lambei which is the focus of this fact file, Lambeosaurus magnicristatus and Lambeosaurus clavinitialis which are also from Alberta, Canada.

Lambeosaurus has seen a significant amount of palaeontological research covering its phylogeny, vocalisation, biostratigraphy, and ecomorphospace. The cranial crest function of Lambeosaurus has also been a focus of research. The 2009 research paper by Evans and co-authors studied brain and nasal cavity endocasts for four lambeosaurine dinosaurs: Lambeosaurus, Corythosaurus casuarius and Hypacrosaurus altispinus. The results of which noted that lambeosaurine brain morphology saw little differentiation in comparison to hadrosaurines.
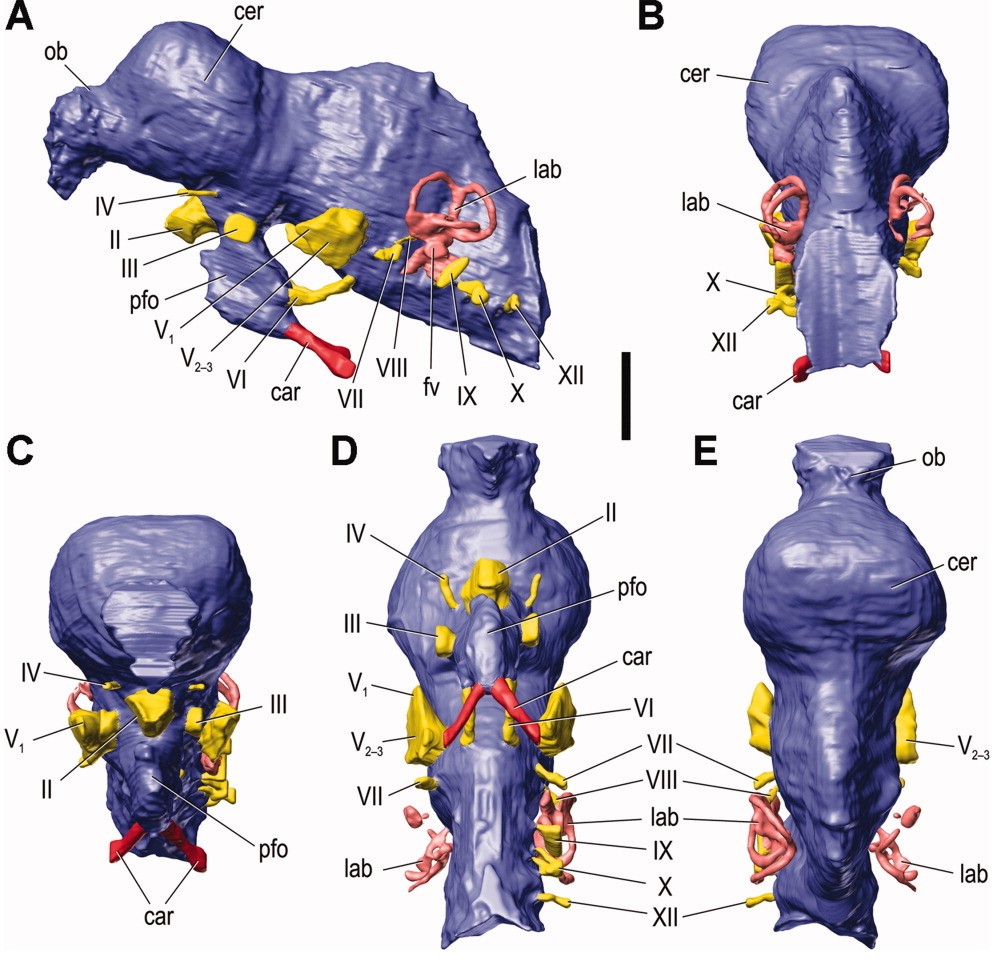
The elongation of the cochlea (inner ear) suggested lambeosaurines had a profound sense of hearing able to recognise low-frequencies, with potential to pick up hypothesised low-frequency calls. The brain of lambeosaurines was greater than most other large dinosaurs, with the cerebrum bigger than those found in big theropods and non-hadrosaurian ornithischians. The large brains of lambeosaurines were consistent with the expected social behaviours interpreted from the crest being used as a social signalling structure.
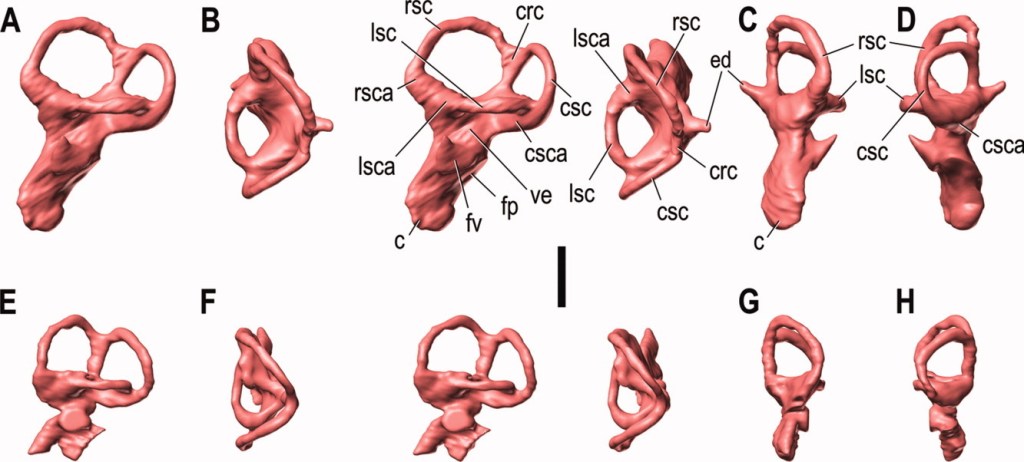
Endocranial anatomy research of lambeosaurines is supplying more insight into crest evolution within Lambeosaurus. The endocasts of the lambeosaurine brain cavity and nasal cavity reconstructions have generated new data on ontogeny and evolution of the nasal cavity.
As a result, vocalisation and nasal vestibule function was found to be more important in lambeosaurine crest evolution. This research is one of the most comprehensive studies to date on sensorineural evaluation of crest functional hypotheses, evaluation of cranial ontogeny and its complex evolutionary history.
Enjoyed this post? Support my science outreach.
References
Lambeosaurus lambei skeletal by Dr. Scott Hartman skeletaldrawing.com.
Dinosaur silhouettes from Phylopic.org by Matt Martyniuk and used under the Attribution Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported license.
